Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Health & Safety Incident Reporting, a fundamental aspect of workplace safety for H&S professionals in the UK.
This guide aims to provide a thorough understanding of the significance and legal requirements of incident reporting, alongside practical steps and strategies to enhance safety in the workplace.
The Significance of Incident Reporting in Workplace Safety
Incident reporting plays an integral role in the proactive management of workplace safety. It involves not only documenting accidents and near misses but also using this data to identify potential hazards and implement preventative measures.
By effectively reporting incidents, organisations can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of workplace incidents, thus safeguarding employee well-being.
Legal Requirements for Incident Reporting under RIDDOR 2013
Adhering to the Reporting of Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences Regulations (RIDDOR) 2013 is a legal requirement in the UK. This regulation mandates the reporting of specific types of work-related incidents, which is crucial for the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) to monitor and investigate workplace risks.
In this guide, we will explore several key areas:
- Understanding Incidents: We will define and differentiate between incidents, accidents, and near misses, emphasising the importance of reporting near misses for hazard identification.
- Benefits of Effective Incident Reporting: This section covers how incident reporting aids in identifying hazards, implementing corrective actions, promoting a safety culture, and reducing incident severity.
- Incident Reporting Process: We’ll provide a step-by-step guide to the incident reporting process, including initial reporting, investigation, and monitoring effectiveness.
- RIDDOR Reporting Requirements: A detailed look at RIDDOR’s specific reporting requirements for work-related incidents.
- Investigating Incidents: We’ll discuss the importance of thorough investigations, outlining key steps involved.
- Corrective and Preventive Actions: This section will focus on the significance of implementing corrective and preventive measures and how to ensure their effectiveness.
- Promoting a Culture of Safety: We’ll explore how incident reporting contributes to fostering a positive safety culture within an organisation.
Before we go further, we recommend downloading our free checklist and step-by-step guide to report incidents correctly.

1) Understanding Incidents
Grasping the nuances between incidents, accidents, and near misses is pivotal for effective health and safety management in any workplace. This understanding is crucial not only for compliance with legal standards but also for fostering a safer work environment.
Defining and Differentiating Incidents, Accidents, and Near Misses
Incidents: In the realm of workplace safety, an ‘incident’ is a broad term that encompasses any unplanned event that could have, or did, lead to injury, damage, or loss. Incidents include both accidents and near misses. They are the indicators of potential hazards in the workplace that, if ignored, can escalate into more serious situations.
Accidents: An ‘accident’ is a type of incident that results in physical harm or injury to a person or damage to property. Accidents are the incidents where the potential risk becomes a reality, often prompting immediate action and investigation to prevent recurrence.
Near Misses: A ‘near miss’ refers to an incident that, under slightly different circumstances, could have resulted in harm or damage. These are critical warning signs and learning opportunities. Near misses are often overlooked, yet they provide invaluable insights into existing workplace hazards without the cost of injury or damage.
Importance of Reporting Near Misses for Hazard Identification
Reporting near misses is a key component in proactive safety management. It allows H&S professionals to identify and rectify potential hazards before they result in accidents. By encouraging a culture where all incidents, especially near misses, are reported and investigated, organisations can significantly reduce the risk of serious accidents occurring.
Each near miss report contributes to a larger safety narrative, allowing for a deeper understanding of the workplace’s unique risk profile. Analysing these reports helps in identifying patterns or areas of concern, which can then be addressed through targeted safety interventions.
This not only helps in maintaining compliance with health and safety regulations but also demonstrates an organisation’s commitment to continuous improvement in safety standards.
2) Benefits of Effective Incident Reporting
Effective incident reporting is not just a regulatory requirement under frameworks like RIDDOR; it is a cornerstone of maintaining and improving workplace safety. This process offers numerous benefits, from hazard identification to fostering a culture of safety.
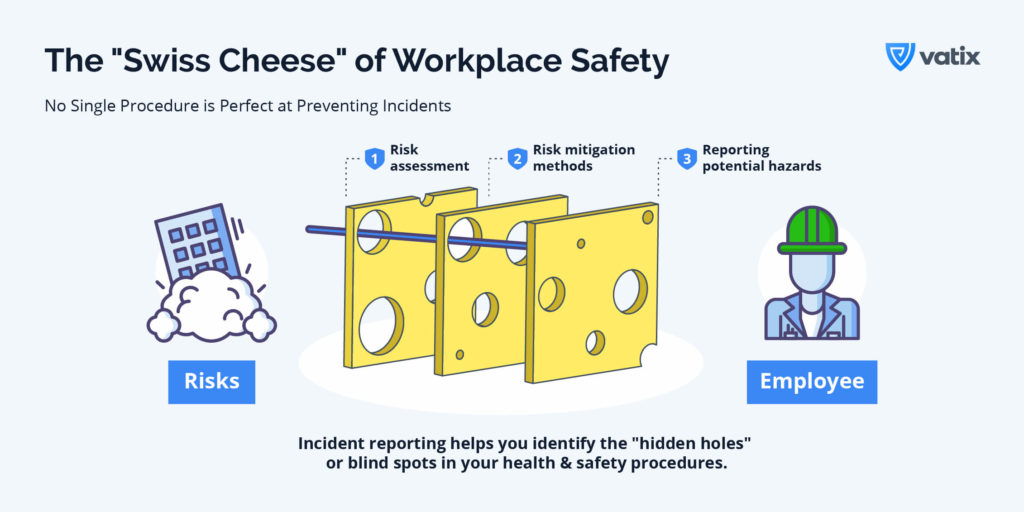
Identifying Hazards and Risk Factors
The primary benefit of incident reporting lies in its ability to uncover hidden hazards and risk factors in the workplace. Each incident report, be it about an accident or a near miss, provides valuable data, enabling H&S professionals to analyse trends and patterns.
This analysis can reveal less obvious risks, offering an opportunity to address them proactively. By identifying these hazards early, the likelihood of incidents, including serious injuries and accidents, is significantly reduced.
Implementing Corrective and Preventive Actions
Incident reports, particularly those detailing serious incidents or dangerous occurrences, are instrumental in guiding the development and implementation of corrective and preventive actions.
These actions, tailored based on specific incident details, are essential in mitigating risks. They range from immediate, short-term fixes to long-term strategic changes in workplace practices and policies.
Effective incident reporting ensures that these actions are not just reactive but also preventive, aiming to stop potential incidents, such as occupational diseases or security breaches, before they occur.
Promoting a Culture of Safety
A robust incident reporting system is a key factor in promoting a culture of safety within an organisation. When employees, from workers to non-workers, understand the importance of reporting incidents and see tangible improvements resulting from their reports, it encourages active participation in safety initiatives.
This creates a positive feedback loop where safety becomes a shared responsibility, leading to higher engagement and awareness among all staff members.
Reducing Incident Frequency and Severity
Consistent and thorough incident reporting leads to a gradual reduction in both the frequency and severity of workplace incidents. As hazards, including potential risks and environmental conditions, are identified and addressed, and as the workforce becomes more safety-conscious, the overall incidence of accidents and near misses decreases. This not only enhances the safety and well-being of employees but also results in financial benefits for the organisation through reduced downtime and lower insurance costs.
3) Incident Reporting Process
A well-structured incident reporting process is vital for the effective management of workplace safety, especially in adhering to legal requirements like those outlined in RIDDOR. This section provides a step-by-step guide, encompassing initial reporting, investigation, and the monitoring of the effectiveness of actions taken.
Step-by-Step Guide to Incident Reporting
- Initial Reporting: The first step involves the immediate documentation of the incident. This includes recording key details such as the date, time, and specific location of the incident, a description of what occurred, and any immediate actions taken. It’s crucial to report incidents, from minor accidents to serious injuries, as soon as possible to ensure accuracy and comprehensive data collection in the incident reporting form.
- Investigation: A thorough investigation follows the initial report. This step is critical in uncovering the root cause of the incident, whether it’s an accident, near miss, or a dangerous occurrence. It involves:
- Gathering evidence, including witness statements and physical evidence from the incident site.
- Analysing the incident sequence to understand how it unfolded.
- Identifying contributing factors, such as environmental conditions, equipment failure, or procedural lapses.
- Root Cause Identification: Determining the root cause is crucial to prevent future incidents. This involves delving into underlying issues that may include organisational processes, safety culture, or training deficiencies. Identifying the root cause helps in addressing the real issues beyond the immediate reasons for the incident.
- Implementing Corrective and Preventive Actions: Based on the findings, appropriate corrective and preventive actions are developed. These actions could range from equipment modifications and process changes to implementing or revising training programs, all aimed at mitigating similar incidents in the future.
- Monitoring Effectiveness: The final step involves assessing the effectiveness of the implemented actions. This is essential to ensure that the actions have effectively mitigated the identified risks and to make adjustments as necessary.
Importance of a Structured Process
A structured incident reporting process ensures systematic and efficient handling of incidents. It not only facilitates compliance with reporting requirements but also aids in building a proactive safety culture. By following these steps, organisations can adopt a thorough approach to workplace safety, leading to a reduction in incidents and creating a safer working environment for everyone involved.
4) RIDDOR Reporting Requirements
The Reporting of Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences Regulations (RIDDOR) 2013 sets out specific requirements for reporting work-related incidents in the UK. Understanding these requirements is essential for compliance and effective health and safety management.
Specific Reporting Requirements for Work-Related Incidents
RIDDOR requires the reporting of the following types of incidents:
- Deaths and Specified Injuries: This includes severe injuries such as fractures (other than to fingers, thumbs, and toes), amputations, injuries leading to permanent loss of sight or reduction in sight, and any injury requiring hospital treatment for more than 24 hours.
- Over-Seven-Day Incapacitation of a Worker: Injuries or accidents that result in an employee being unable to perform their normal work duties for more than seven consecutive days (excluding the day of the incident) must be reported.
- Non-Fatal Accidents to Non-Workers: Incidents involving members of the public or people who are not at work (e.g., visitors, customers) which lead to an injury requiring hospital treatment.
- Occupational Diseases: Certain diagnosed industrial diseases linked to specific occupational activities or exposures, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, severe cramps, occupational dermatitis, or occupational asthma, must be reported.
- Dangerous Occurrences: Certain near-miss events with the potential to cause serious harm or damage, such as the collapse of load-bearing parts of lifts and lifting equipment, electrical short circuit causing fire or explosion, or accidental release of a biological agent, are reportable under RIDDOR.
When and How to Report
Incidents should be reported to the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) as soon as possible. Reporting can be done online through the HSE website or, for fatal and specified injuries only, by telephone. It’s important to maintain accurate records of any reportable incident, including the report reference number, for at least three years.
The Role of RIDDOR in Workplace Safety
RIDDOR’s reporting requirements are critical in helping the HSE and other authorities identify where and how risks arise in the workplace. This information is used to investigate serious incidents and to inform the development of new legislation and guidance, ultimately improving workplace safety standards across the UK.
5) Investigating Incidents
Thoroughly investigating workplace incidents is crucial for understanding why they happened and how similar events can be prevented in the future. A well-conducted investigation provides the foundation for implementing effective corrective measures and is integral to an organisation’s overall health and safety strategy.
Importance of Conducting Thorough Incident Investigations
Investigating incidents, especially those that could or did lead to serious injury or damage, helps in identifying not just the immediate causes but also any underlying issues. It allows organisations to examine and review their health and safety policies, procedures, and practices, ensuring they are effective and fit for purpose.
Key Steps in Incident Investigations
- Immediate Response and Securing the Scene: The first step is to respond to the incident promptly to ensure the safety of all personnel and to secure the scene. This prevents further incidents and preserves evidence.
- Gathering Evidence: Collecting evidence is crucial for a thorough investigation. This includes taking photographs of the scene, collecting physical evidence, and recording witness statements.
- Analysing the Incident Sequence: Investigate the sequence of events leading up to the incident. This analysis helps identify what happened and how it happened.
- Identifying Contributing Factors: Look beyond the immediate causes and identify contributing factors. These could include equipment failure, environmental conditions, human error, or organisational factors.
- Determining Root Causes: The goal is to determine the root causes – the underlying reasons why the incident occurred. This might involve reviewing workplace procedures, safety protocols, training, and maintenance records.
- Reporting Findings: Documenting the investigation’s findings is critical. This report should be clear, concise, and include recommendations for preventing similar incidents.
- Implementing Changes: Based on the findings, implement changes to prevent recurrence. This could involve changes in procedures, training, equipment, or even workplace culture.
- Follow-Up: Regularly review the effectiveness of the changes made to ensure they are working as intended and modify them if necessary.
Effective incident investigations are a learning tool, helping to prevent future incidents and fostering a culture of continuous improvement in health and safety standards.
6) Corrective and Preventive Actions
Implementing corrective and preventive actions in response to incidents is a vital aspect of workplace health and safety management. These actions not only address immediate issues but also prevent future occurrences, thus playing a crucial role in maintaining a safe working environment.
Significance of Implementing Corrective and Preventive Actions
Corrective actions are responses to identified problems, implemented to rectify and mitigate the effects of an incident. Preventive actions, on the other hand, are proactive measures taken to eliminate the causes of potential non-conformities or incidents. The implementation of these actions is significant because they:
- Address Immediate Safety Concerns: Corrective actions help to quickly resolve safety issues that could lead to further harm or damage.
- Prevent Future Incidents: By addressing the root causes of incidents, preventive actions reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
- Enhance Safety Protocols: Implementing these actions often leads to improvements in safety protocols, equipment, and training.
- Promote a Proactive Safety Culture: A proactive approach to safety, where potential risks are identified and addressed before they lead to incidents, is fostered.
Guidance on Developing Effective Corrective and Preventive Actions
- Root Cause Analysis: Effective actions begin with a thorough analysis of the incident to identify the root cause.
- Developing Action Plans: Develop specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) action plans to address the root causes.
- Involvement of Employees: Engaging employees in the development and implementation of these actions ensures practical and effective solutions.
- Training and Communication: Ensure all relevant staff are trained and informed about the new measures.
- Monitoring and Review: Regular monitoring and review of the effectiveness of these actions are vital. This helps in making necessary adjustments and improvements.
Importance of Monitoring Action Effectiveness
Monitoring the effectiveness of corrective and preventive actions is as important as their implementation. Regular reviews help ensure the actions work as intended and effectively reduce risks. It also provides an opportunity for continuous improvement, keeping safety protocols up-to-date and relevant.
In summary, the implementation of corrective and preventive actions is a critical step in incident management. Not only do they address immediate concerns, but they also lay the groundwork for a safer and more secure working environment.
7) Promoting a Culture of Safety

Creating and maintaining a culture of safety in the workplace is pivotal for the well-being of employees and the overall health of the organisation. Incident reporting plays a fundamental role in fostering this culture, as it is integral to understanding and mitigating workplace hazards.
Role of Incident Reporting in Fostering a Positive Safety Culture
Incident reporting is more than a procedural necessity; it’s a key driver in promoting a proactive approach to safety. By encouraging the reporting of incidents, especially near misses and minor accidents, organisations can gather crucial information about potential risks and hazards in the workplace.
This practice helps identify specific areas requiring attention, from environmental conditions to occupational health concerns.
Open Communication and Reporting Without Fear of Blame
A positive safety culture is underpinned by open communication. Creating an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting incidents without fear of blame or retribution is essential. This openness not only improves the accuracy and frequency of reporting but also encourages a collaborative approach to safety, where every person involved plays a role in identifying and mitigating risks.
Employee Involvement in Safety Initiatives
Involving employees in safety initiatives and the incident reporting process is critical. This involvement can range from participating in risk assessment exercises to contributing to the development of incident report forms and procedures. When employees are actively engaged in these processes, they are more likely to buy into the safety culture, understand its importance, and adhere to established protocols.
Continuous Improvement and Learning
An effective safety culture is dynamic and evolves through continuous learning and improvement. Analysing incident reports, especially those involving serious injuries or dangerous occurrences, provides valuable lessons. These insights lead to the development and implementation of effective corrective measures, further information sharing, and regular reviews of safety practices.
Conclusion
In summary, promoting a culture of safety through effective incident reporting is not just about compliance with regulations like RIDDOR but about cultivating an environment where safety is deeply embedded in the organisation’s ethos. It involves a commitment to transparency, continuous learning, and employee engagement, all of which are essential for creating a safe and healthy working environment.
Make Incident Reporting a Breeze in Your Organisation
If you’d like to discover how our incident reporting tool can make it easier to streamline incident reporting in your organisation, contact us to get a demo.
Don’t forget to also take advantage of our free checklist and step-by-step guide on how to report incidents.
For a handy summary of this incident reporting guide, print out the infographic below and share it with others who can benefit from it.



